Web Design (Picasso)
- Level High School
- Contact Hours 140
- Timeframe Year
This is a project-based course that teaches students how to build their own web pages. Students will learn the languages HTML and CSS, and will create their own live homepages to serve as portfolios of their creations. Students will finish this course with tangible, professional, mobile responsive websites.
To view the entire syllabus, click here or click to explore the full course.
|
Getting Started - What is the Web?
Students are provided with a high-level introduction to the Internet and how it functions, investigate how the Internet has impacted society over time and set course goals for themselves. |
|
HTML - Structuring Websites
Students learn about the language behind all websites: HTML. Students learn about several different HTML tags as well as the basic structure of a web page. Students use HTML to develop several of their own creative web pages. |
|
CSS - Styling Websites
Students learn the language CSS and use it to style their web pages. Students learn about the benefits of styling with CSS and will use CSS to create several styled web pages of their own. |
|
Project - Create Your Homepage
Students build their own websites about themselves. This site will be accessible on their own custom domain and will be continually improved by the student as they continue on in the course. It will serve as a running portfolio of each creative project they create in the course. |
|
Advanced HTML and CSS
This module dives deeper into different things we can do with HTML and CSS. Students practice advanced topics in HTML and CSS, including visibility, image filtering, interaction, and animation, to develop more advanced websites. |
|
Project - Tell a Story
Students develop an animated and interactive web page that tells a visual story and add this web page to their personal portfolio website. |
|
Bootstrap
This module introduces students to Bootstrap, an HTML and CSS framework for developing responsive, professional websites. Students use Bootstrap to develop several professional, mobile responsive websites. |
|
Bootstrap Project
In this project, students work in teams to create a professional, responsive website using Bootstrap. |
|
Designing User Interfaces
This module introduces students to the theory and practice of user interface design. Students learn about what makes an engaging and accessible user interface and will employ an iterative design process including rapid prototyping and user testing to design and develop their own engaging web pages. |
|
Final Project
In this project, students work in teams to design, prototype, test, and develop a final website. |
Explore programs that your students will build throughout this course!
Here are a few examples of teacher resources and materials to use in the Web Design (Picasso) course
The CodeHS Web Design Level 1 Certification offers high school students the opportunity to validate their mastery of Web Design, giving them a competitive advantage when entering college or the workforce.
Learn More
Web Design (Picasso) is aligned with the following standards
| Standards Framework | View Alignment |
|---|---|
| Certiport IT Specialist HTML and CSS | View (88.2%) |
| ISTE | View (71.4%) |
| CIW Site Development Associate Exam | View (70%) |
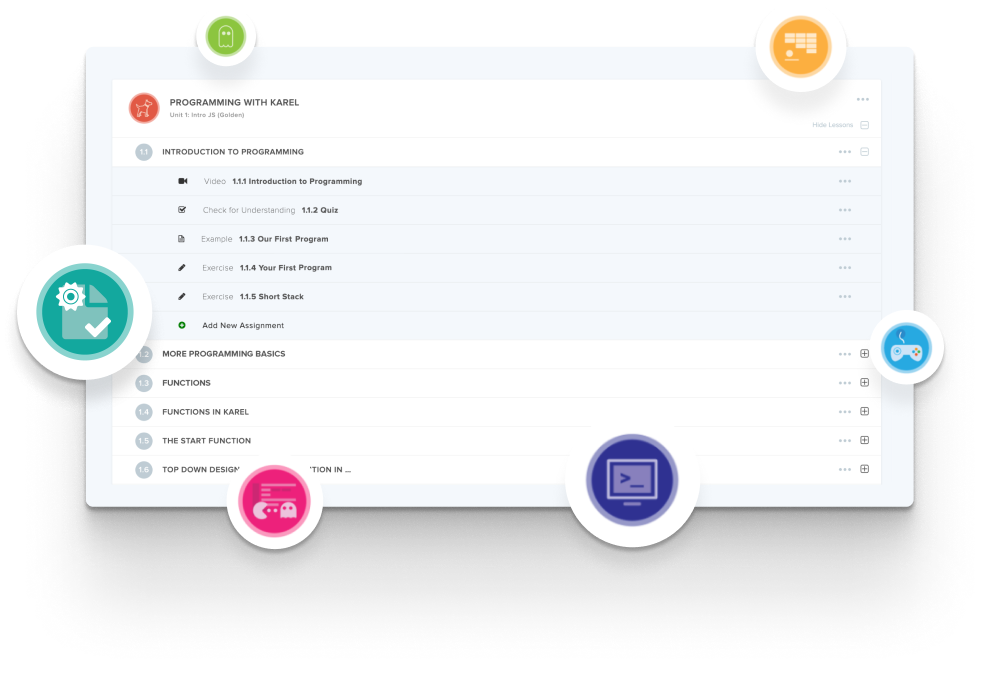
Create and organize Assignments in any CodeHS course that you're teaching. You can even add custom assignments to pre-existing CodeHS courses.
Learn MoreDidn’t find what you were looking for? Here are a few links that might be useful to you.